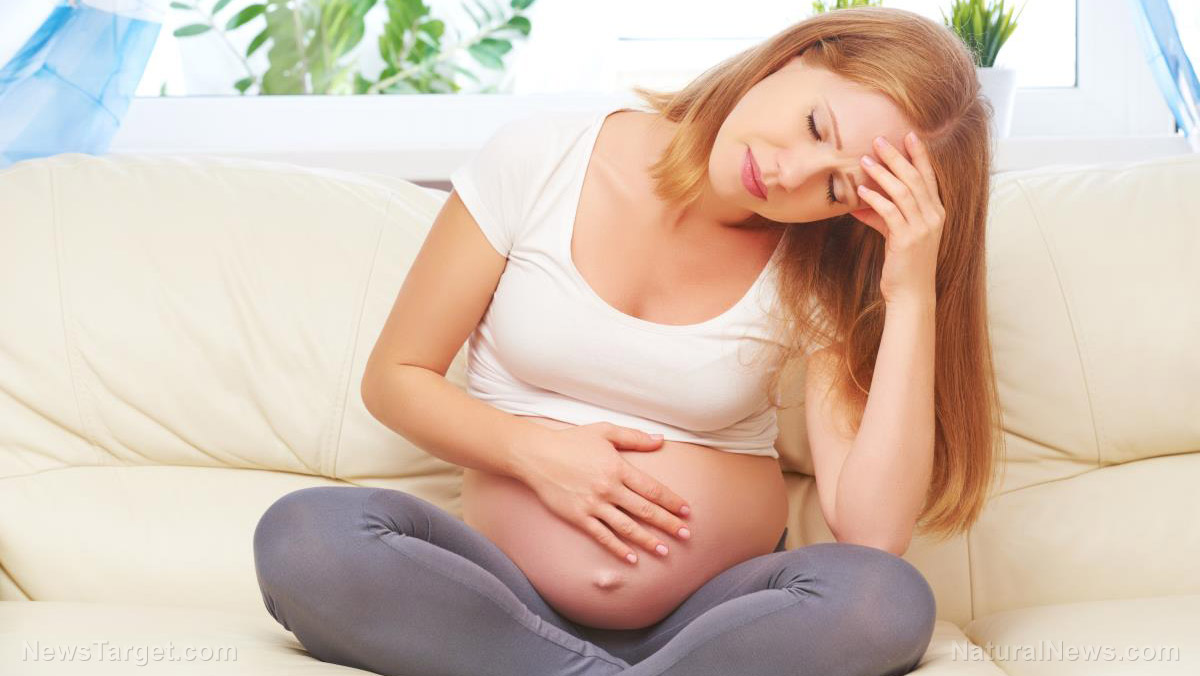
NEW EVIDENCE: In pregnant women, COVID vaccine mRNA targets the placenta, the umbilical cord blood and the fetus
02/26/2024 / By Lance D Johnson
A peer-reviewed study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology presents new evidence on the harms of the COVID vaccine in pregnant women and their babies. For the first time, researchers show how the COVID-19 vaccine mRNA can infiltrate the umbilical cord blood and penetrate the fetal-placental barrier, targeting the uterus and the developing fetus with foreign spike proteins.
COVID-19 vaccine mRNA does not simply degrade in the deltoid muscle
When explaining the safety of their mRNA vaccines, the manufacturers assure that the mRNA degrades in the deltoid muscle of the vaccine recipient, leaving them with a robust immune response. This false assurance has been debunked by independent scientists more than once.
Not only does the injected mRNA escape the injection site, but it can “spread systemically” to the placenta and the umbilical cord blood of fetuses. The latest research shows that the alleged vaccine is not an immunization at all, but more so a weapon that targets reproduction and future generations of people. The mRNA’s ability to target the placenta was already published before the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccines.
After the mRNA reached the reproductive system of pregnant women, researchers were able to detect spike proteins in placental tissue. The mRNA not only crosses the fetal-placental barrier, but it also remains bio-active, forcing the body to produce toxic spike proteins in areas of the body where natural biological processes are necessary for sustaining life.
“The primary objective of the study was to investigate the knowledge gaps surrounding mRNA therapies during pregnancy, utilizing the COVID-19 vaccine as a foundation for future mRNA therapeutic developments, given its established use,” said the study’s corresponding author, neonatologist Dr. Nazeeh Hanna.
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are a threat to pregnant women and babies
This preliminary yet groundbreaking research was conducted on two pregnant women and their babies. Patient One is a 34-year-old woman who was vaccinated with two doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and two additional boosters, one from Moderna and one from Pfizer. Two days before the delivery of her baby via cesarean section, Patient One was injected with the Moderna mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
Right away, the researchers found a “notably high signal” of vaccine mRNA in the placental decidua tissue, which is the specialized endometrium layer that forms the base of the placental bed. The vaccine mRNA was also detected in the cord and maternal blood samples. This could lead to runaway spike protein synthesis in sensitive areas of the body, which can have undesirable effects in the reproductive system and potentially damaging effects in the cellular, hormonal and genetic development of the offspring.
Patient Two is a 33-year-old woman who received two doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. The second dose was administered 10 days before the vaginal delivery of her baby. When the researchers analyzed the placenta, they found biologically active spike proteins. The vaccine mRNA had effectively migrated through the blood and across the fetal-placenta barrier, where it was hijacking the normal protein synthesis of the cells.
Further analysis found that the vaccine mRNA was localized in the villus stroma, which is the connective tissue layer that supports the fetal capillaries and villous trophoblast. This is a concerning development, considering that the villous trophoblast is the primary barrier between maternal and fetal tissues. This barrier is responsible for the exchange of nutrients between a mother and her fetus.
According to the study, it took two days for the vaccine mRNA to reach the placenta and translate the spike proteins, inevitably harming the placental tissue and the healthy development of the fetus in the process. When the vaccine mRNA re-codes the fetal cells to produce foreign spike proteins, the fetus does not have access to the proteins that are necessary for their healthy development.
The mRNA doesn’t create an adequate immune response to the spike proteins that it translates, either. According to the analysis, the continuity of the vaccine mRNA (which is necessary to activate an immune response) varied across different samples. The mRNA was largely fragmented in the cord blood and more stable in the placenta. In Patient One, only 23% of the mRNA was still intact. In Patient Two, approximately 42% of the initial integrity of the mRNA was retained. In Patient One, the integrity of the mRNA was 85% in the maternal blood. By the time it made its way to the cord blood, it had degraded to 13% viability.
Pointing to the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS), Dr. Hanna said there have been “reports of infants dying from thrombocytopenia (low platelets) following maternal vaccination.” She said there is also “evidence of infants having heart attacks in the womb following maternal vaccination.” She added, “None of this is new information. It has simply been widely and systematically censored.”
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
biodistribution of spike proteins, bioweapons, Censored Science, chemical violence, conspiracy, cord blood, deception, depopulation, developmental disorders, heart damage, infant health, medical violence, placenta, pregnancy, protein synthesis, research, science deception, spike proteins, thrombocytopenia, uterus, vaccine injury, vaccine mRNA, vaccine wars, vaccines, women's health
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author